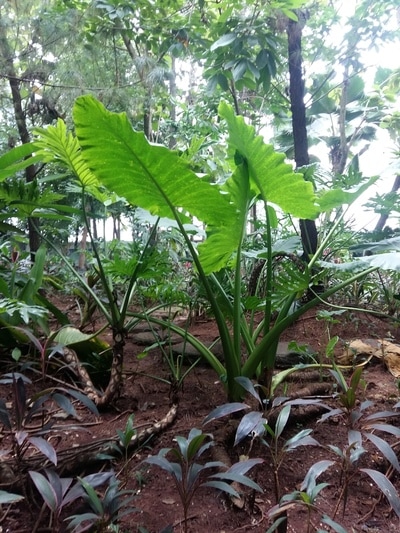
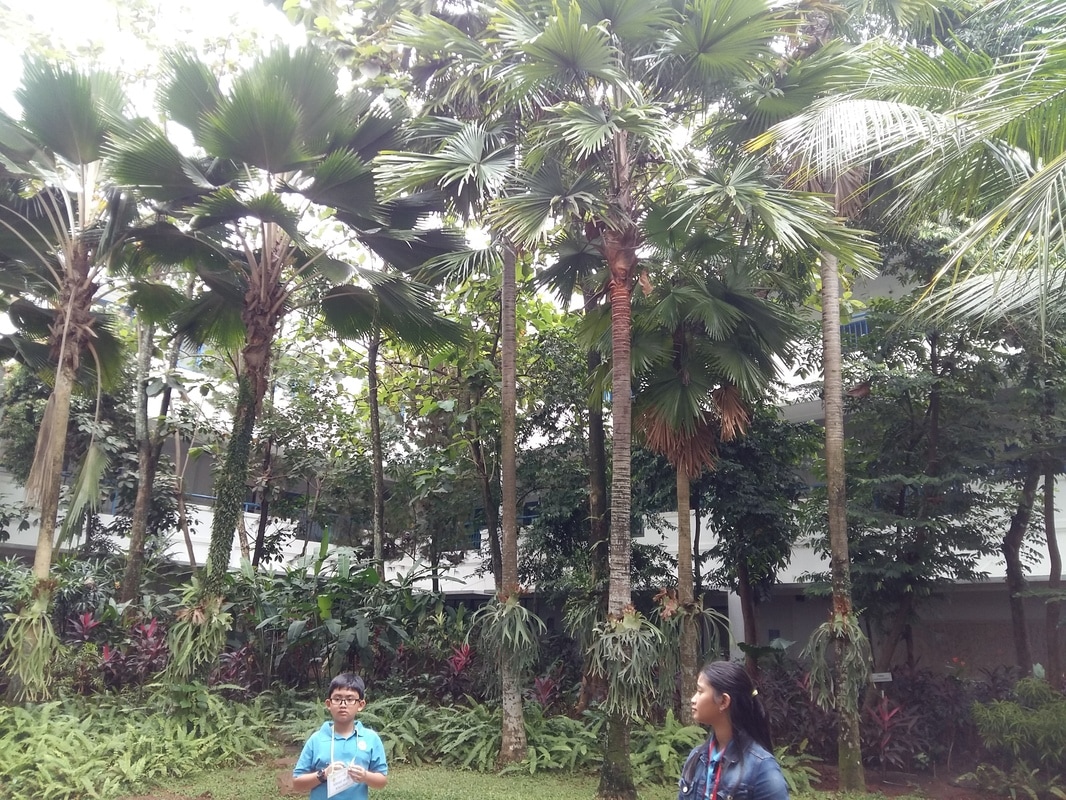
Plants to break the stream of rain water to prevent flood
Correlation between tree architecture models,soil and water conservation at al-jabr school
Research objectiveThe objective of the research is to find out the influence of plant A and plant B on stem flow,through fall,surface run off, infiltration, as well as an erosion and soil physical property.
Research benefit
This study is expected to provide information that accelerate restoration process by focusing on selecting species that can effectively control water runoff and soil loss, as well as on designing effective vegetation restoration pattern.
Research exploration
1.Tree Architecture models
2.Soil water balance 3.Water erosion 4.Factors affecting water erosion (Climate,topography,plant cover) 5.Soil properties 6.Experiments Material and methods Material and equipment Methods: 1.Tree architecture model identification 2.Stone's model 7.Interpretation data of experiments Vegetation measurement 1.Basal area measurement 2.Tree diameter and height measurements 3.Soil conservation parameter measurement (Rainfall,through fall,Stem flow) 4.Erosion and run off measurements 5.Interpretation data (simple data analysis). |
Central Idea : Biodiversity relies on maintaining the interdependent balance of organisms within systems
Key concept: causation, connection, responsibility Related concept: Balance; Biodiversity; Interdependence Strands (Knowledge) : Living things Attitude: Appreciation, Enthusiasm, Independence Lines of Inquiry: • Ways in which ecosystems, biomes and environments are interdependent • How human interaction with the environment can affect the balance of systems • The consequences of imbalance within ecosystems Learning outcomes
Mentor's questions:
1.What are plants? 2. Student's questions: 1.What is living thing and what is non-living thing? 2.What does a plant need? Why? |
Mentors and group members
LO 1:Describe the interactions of living things within and between ecosystems.
Exploring,wondering and questioning-Beginning with what students know about the plants
Exploring,wondering and questioning-Beginning with what students know about the plants
interdependence among organisms
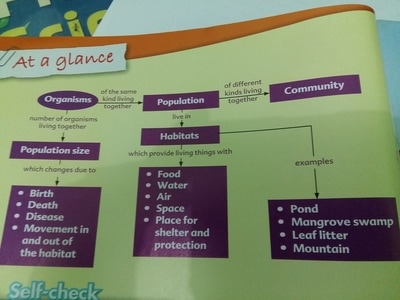
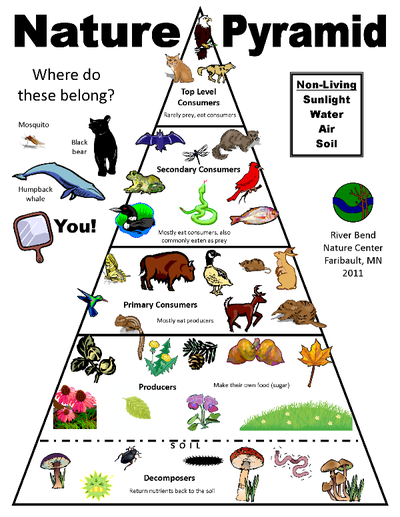
At school area showed many different habitats found there include a garden, a tree, a flower, a pond or log. Each habitat is different and some organisms.
All the populations living in a habitat depend on on another for survival. We say they interdependent. Plants depend on insects such as butterflies and bees to pollinate their flowers. Other plants depend on animals to help disperse their seeds. Animal waste also enriches the soil, making it fertile for plants to grow well. An organism is a living thing A population is a group of organisms of the same kind that live together and reproduce in a particular place. |
(The role of prior knowledge in learning)
1. Students mind map their thinking about central idea. 2.The Known and the Unknown chart (students are able to reflect what they know the plants as their specific topic), its completed individually. 3: Getting organized graphically 4.Visual sequencing 5.Visualizing cause and effect 6.The whole pie Community
What does community consist of? population do not live a lone. They share the environment with other populations. All the different populations of organisms that live together in a habitat form a community. The grass in a mini jungle at school form a community with the warms, snails, and insects. We can find some different communities that can be found in different habitats. "Eco" means environment. In ecosystem, the organisms interact with one another and with their physical environment. This interaction forms a system. A healthy ecosystem includes various types organism interacting with one another and with the physical environment. |
School's habitats
Man-made habitats are called artificial habitat. These place provide the organisms living thing in them with environment that is suitable for them to survive in.
The place where an organism lives is called habitat. Habitats provide living things with everything that they need to survive. They need food to produce energy, to live and grow. They need water to drink and air to breathe. They also need space and place where their young can find shelter for protection. Explore the plants and soil
The inquiry emanates from a question, problem or exploration that has meaning to students
Making observations Look at the plants Seeing,feeling around us (We seek questions and answer about phenomena of plants). 1.Keep a photo journal of each plant |
Focus on topic inquiry
Students observed and identified correlation between tree architecture models, soils, and water around the school. we can found different of plants in area mini jungle. 1.Students were able to identified various trees canopy. 2.Soil erosion by water 3.Determine the influence the tree architecture models. 4.Description the tree architecture models based on the type of branching and canopy shape. 5.Experiments proposed |
Main ideas of articles: 1. Tree architecture models are a useful tool in the description of tropical trees. Focus on inquiry What matters about this topic? What are the issues surrounding this topic? What are the questions, and/or what problems are unresolved? |
LO 2: Examine interactions between living things and non-living thing parts of the environment.
|
Jig-saw Reading
Reading the articles/paper which has the same research project as the reference resources to enhance student's knowledge. at the end, the students shared the main ideas and supporting detail each of the paragraph. Meet the expert biologist in LIpi Cibodas
Field trip to lipi cibodasField trip to LIPI BOGOR
|
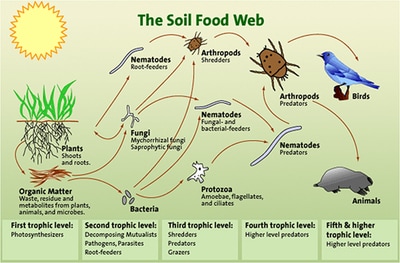
Field community We take a closer look, we will see many kinds of plants and animals in a field community. Some animals live among the plants in the field, while other animals can be found in the soil. Spiders living among the plants in the field, feed on flies. What else do spiders feed on? Earthworms can be found in the soil. How are they beneficial to plants? What do they feed on? Do they have predators? Garden community Our school garden is excellent place to study the common animals and plants living there. Caterpillars feed on leaves to survive. They need a large amount of energy for the later pupa stage. Pond community A pond is an aquatic habitat. It is a good place to study how different populations depend on one another for survival. Water plants are source of food for some aquatic animals. They also provide shade and shelter for the animals and their eggs. Just like animals and plants on the land, aquatic animals also depend on each other for oxygen and carbon dioxide. Besides plants and animals, there are also some micro-organism living in the pond. These micro-organisms are only visible under a microscope. Single plant community Not all habitats are as big as a field or pond. Sometimes, a single plant like a banana or sweet potato plant can be a habitat for many different populations of plants and animals. Communities in other habitats There are many other habitats where organisms live. Some of these habitats include forests, mountains,and rotting logs. A rotting logs is a source of nutrients for some organisms such as fungi. What other organisms can you find here? A Field Trip to LIPI Cibodas One of our inquiries in this project is about plants-how plants interactions of living things within between ecosystem, how they grow. The students understood what kind data they were looking for; Later the students looked at the photographs of our trip and discussed what they have done, why and what we had seen. After collecting and analyzing data, students can naturally proceed to the next step in the process of inquiry, which is demonstrating and presenting their ideas and conclusions. But to find meaning in this information, they need to organize what they find and communicate a specific conclusion Use photo series and data banks to demonstrate conclusions. Photo series work especially well for conclusions about cause and effect:
|
LO 3: Recognize that solar energy sustain ecosystems through a transformation of energy
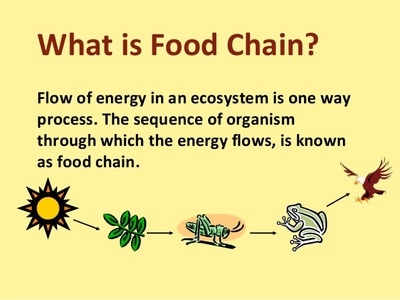
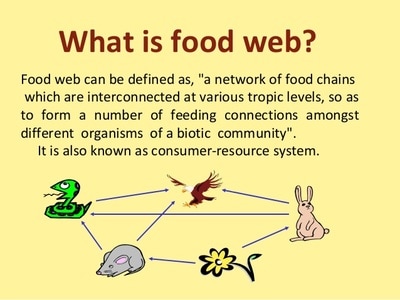
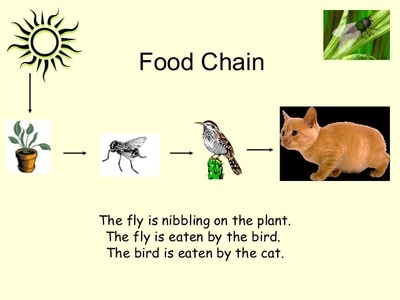
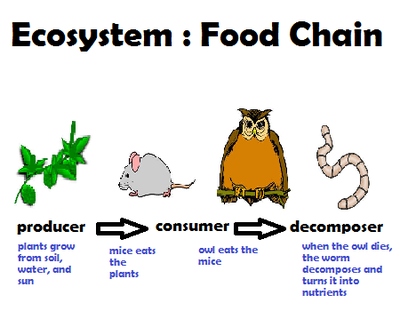
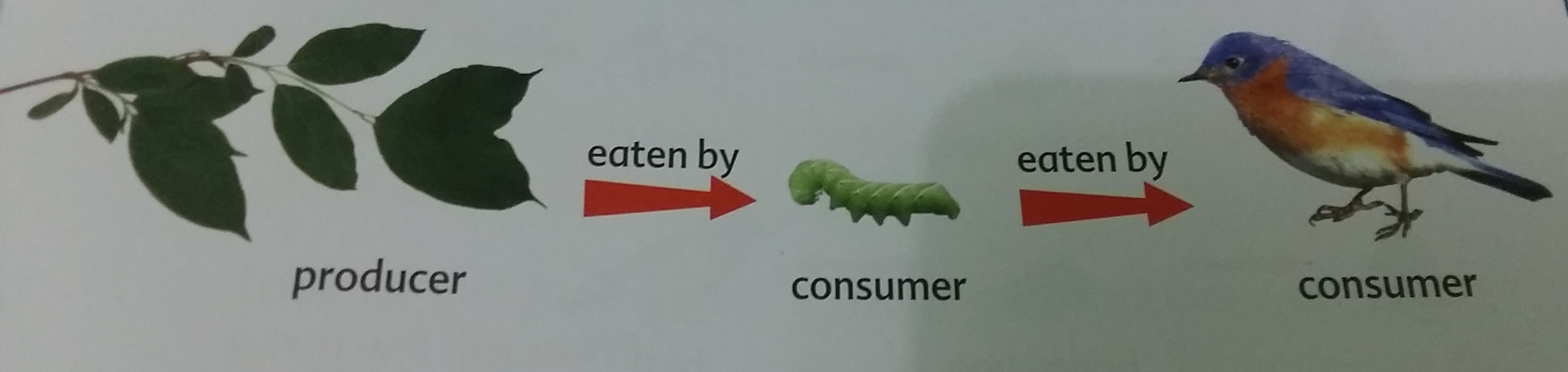
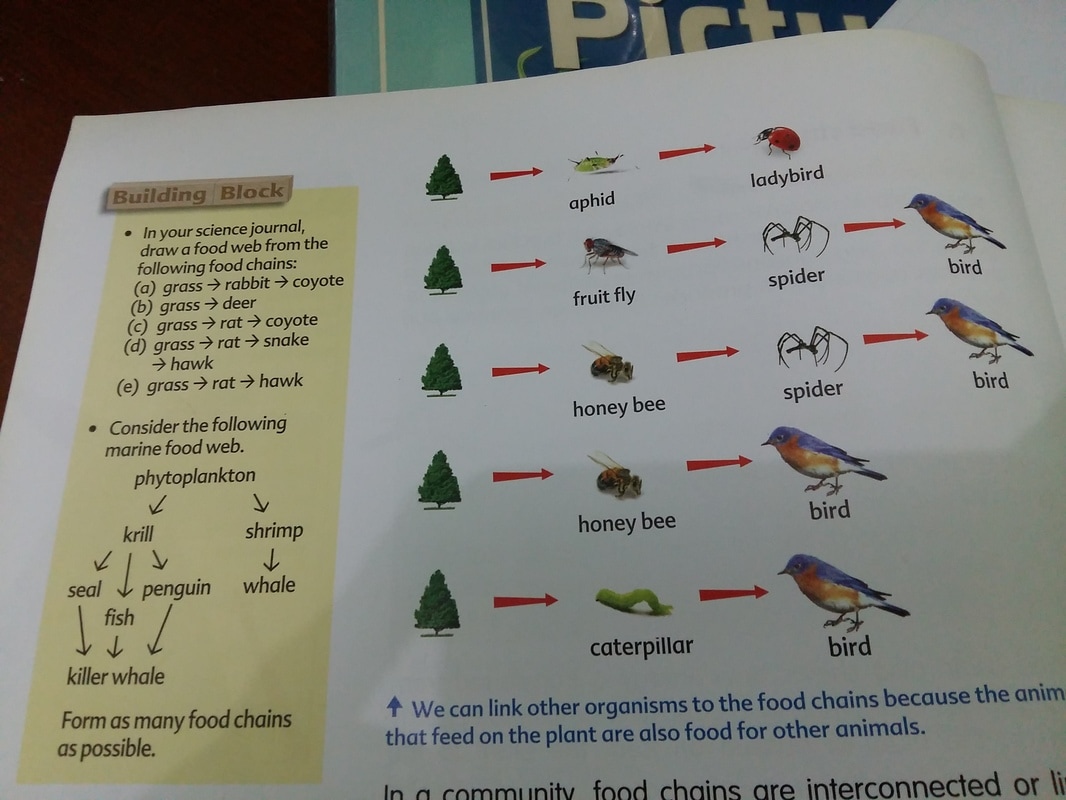
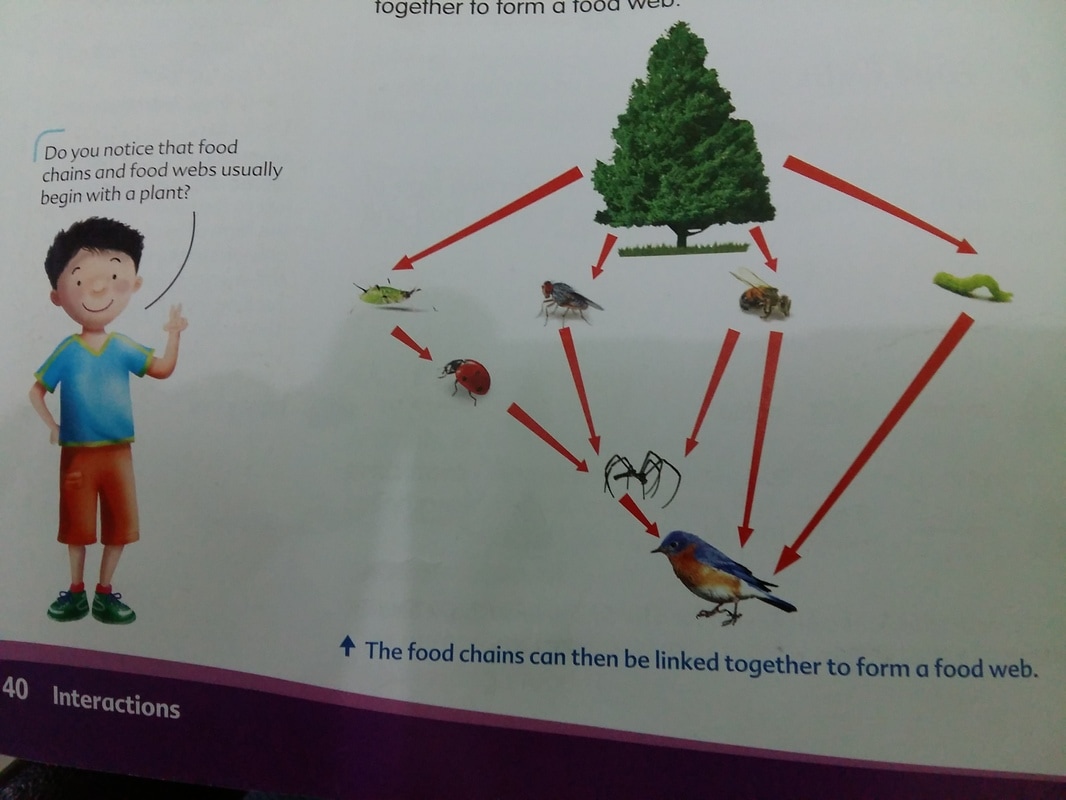
We can link other organisms to the food chains because the animals that feed on the plants are also food for other animals.

From this example, we can see that when there is an increase or decrease in the number of a predator or prey, the number of other organisms in the food chain will be affected
In a food chain or food web, the populations of all the producers and consumers are kept in balance.
In a food chain or food web, the populations of all the producers and consumers are kept in balance.
H.De composers
Energy from the plant gets passed to animals.
But where does the energy go to when the animals die.
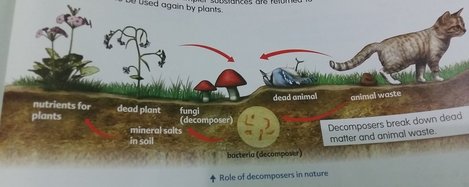
When plants and animals die, they become food for other organisms. These organisms are called decomposes. Decomposes get their food by breaking down dead matter and animal wastes into mineral salts, water and carbon dioxide. Most of these simpler substances are returned to the soil to be used again by plants.
De composers, play a very important role in nature. They prevent earth from being covered by dead matter and animal waste. at the same time, they enrich soil with nutrient for plats to grow.
Energy from the plant gets passed to animals.
But where does the energy go to when the animals die.
When plants and animals die, they become food for other organisms. These organisms are called decomposes. Decomposes get their food by breaking down dead matter and animal wastes into mineral salts, water and carbon dioxide. Most of these simpler substances are returned to the soil to be used again by plants.
De composers, play a very important role in nature. They prevent earth from being covered by dead matter and animal waste. at the same time, they enrich soil with nutrient for plats to grow.
Meet a guest Speaker
|
Tree which has a large leaves is more effective to be planted, because it will prevent the flood, instead of that its good to absorb water and also able to manage the break of rainfall to the surface of ground.
|
Discussion point with the students:
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Experiment 1
Influence of canopy architecture on stem flow at school
|
Rainfall event on a tree can be partitioned into through fall, interception loss and stem flow.In this experiment, stem flow was measured for 3 periods rainfall events of 3 trees each, belonging to banana tree, pine tree, and Damar tree. Diameter of selected.
Maximum stem flow volume recorded for banana tree was 800 ml. The generation of higher stem flow volume in case of banana tree due to concave orientation of branches and leaves. Minimum stem flow recorded is pine tree was 150 ml. |
|
|
|
|
Experiment.2
|
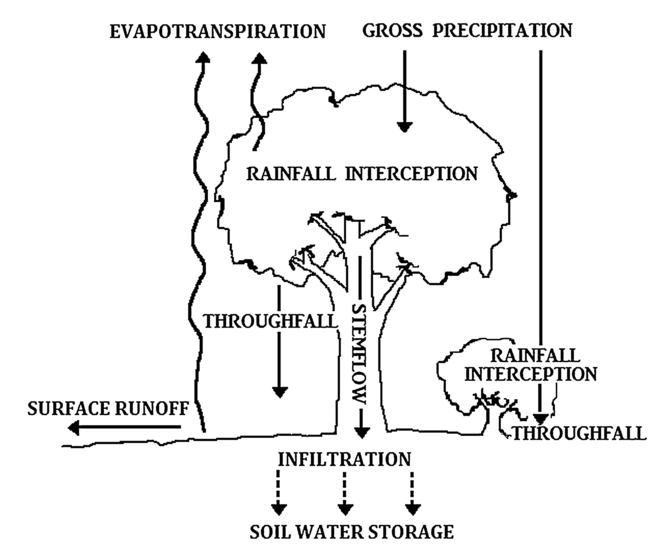
Picture above is a model of canopy interception
Rainfall that falls on canopy can disperse in two ways: canopy evaporation and through fall+stem flow. 1. Canopy evaporation, where part intercepted rain directly evaporates into the atmosphere. 2. Stem flow,where a portion of the rain that comes in contact with canopy flows through the stem, before finally reaching to the ground. 3.Through fall, where the rain reaches the ground through gaps in the canopy or via water that drips from leaves. 4.Modelling the water balance of a site therefore requires quantification of the rainfall intercepted by vegetation as well as estimation of the through fall. 5.Interception, Water abstracted from gross precipitation by leaves and stems of a vegetation canopy and temporarily stored in its surfaces. 6.Interception loss, intercepted lost by evaporation to the atmosphere before reaching the soil surface. |
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Taking action
|
Exhibition Day
|