Students
Mentors
Exploring, Wondering and Questioning
|
This group was focus on paddy field ecosystem. For their topic issues, they want to explore more about Tomcat. Known as the rove beetle (in English), this insect is one of the influence organism in the ecosystem. As what reported currently, this insect was known dangerous and responsible for the attacked of human residents causing mass panic several years ago.
The students start to identify the topic by exploring information through articles, internet, discuss with mentors, formulating questions and observing through pictures. |
|
Researching information and Collecting Data
Excursion to Bogor Agricultural University (IPB)
|
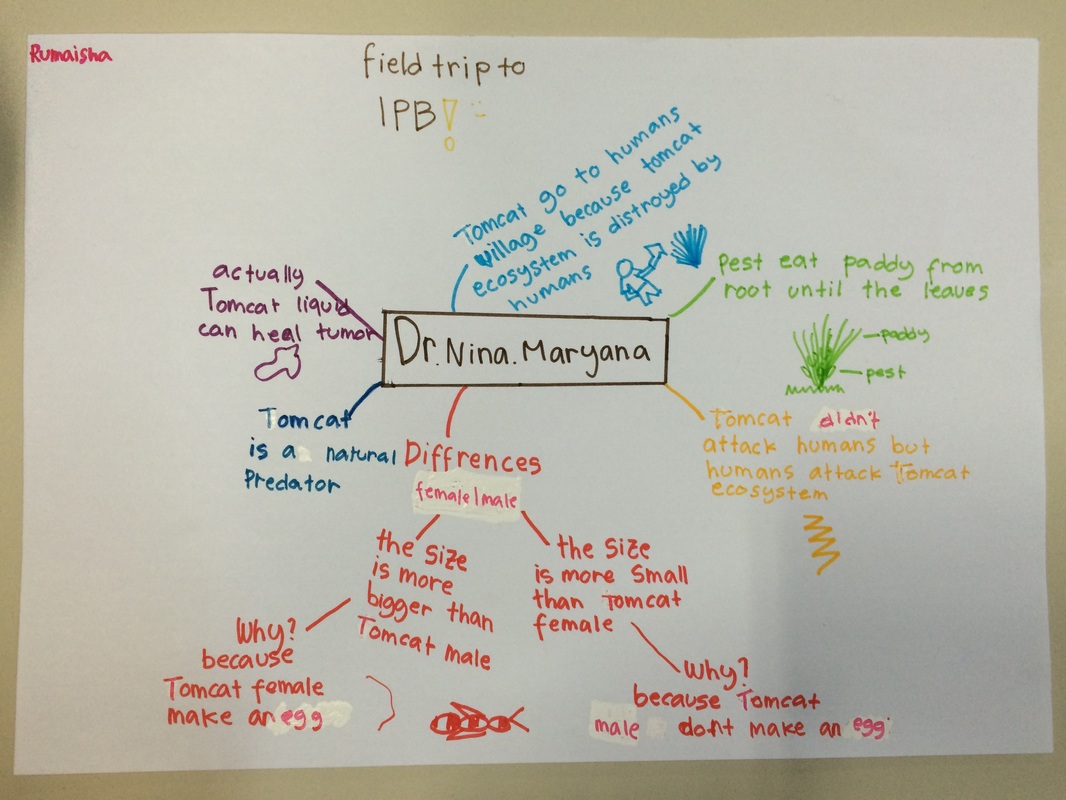
To gain more information about Tomcat, we visited Faculty of Agricultural, Bogor Agricultural University (IPB) to meet and interview one of the insect expert there. She is Ibu Dr. Ir. Nina Maryana Msi, one of the Lecturer of Pest and Plant Disease from The Departement of Plant Protection. Our purpose is to collect more information about what is Tomcat and it's influence within the paddy field ecosystem. We found out that, Tomcat scientific name is Paederus. They showed us video about Paederus, let us explore and doing observation in the insect laboratorium and visiting the insect museum. We also got a chance to visit paddy field ecosystem near the campus to explore and observe more of what paddy field ecosystem looks like.
|
|
Reflection from IPB
Excursion to dinas pertanian & perikanan depok
|
Our next resources was Dinas Pertanian & Perikanan Depok. We went to this place to collect information about paddy field ecosystem existence in Jakarta and surrounding areas. We also want to know the data of resident areas that were reported attacked by Tomcat. After the interview session, Bapak Chudori as the officer from Dinas Pertanian, offered us to visit another paddy field ecosystem that supervise by Dinas Pertanian. We were able to meet the farmer there and explore paddy field again. This is the second time we visited paddy field ecosystem but with different experience because the areas were more muddy and watery.
|
|
Reflection from Dinas pertanian
experimenting and playing with possibilities
Tomcat is the natural predators for Wereng. For our experiments, we want to prove the food chains between Tomcat and Wereng. Since in rainy season Tomcat rarely found and Wereng also hardly found in the paddy ecosystem we visit, so we change the organism. We collected other paddy's pests such as grasshoppers, walang sangit and snails. We use botanical/organic pesticides to control the pests invasion.
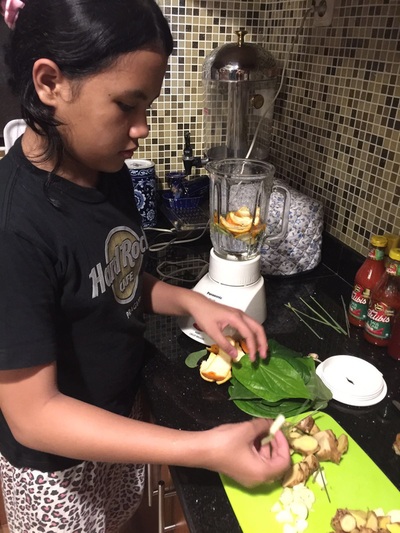
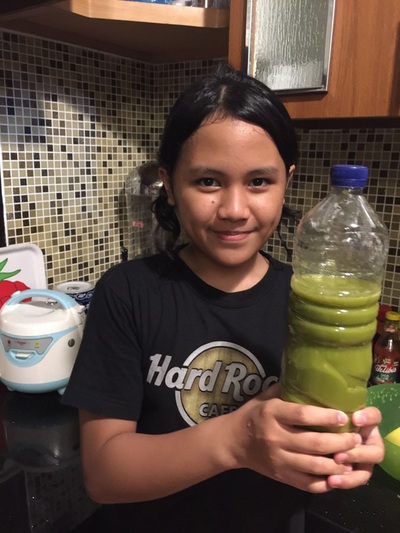
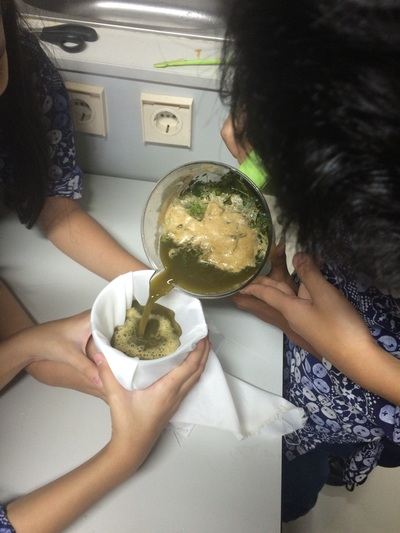
Based on our internet literature research, we found out that lots of plants use as organics pests control. But, we have to sort out the plants that can effectively get rid of pests like grasshoppers and walang sangit. Several of them are actually ingredients from household kitchen such as garlic, lemongrass, ginger, galangal, lemon, betel leaf, etc. These plants contains with essential oils that has low toxic and safe for the host plants. We also found out soursop leaves extract are beneficial to repel grasshoppers. So, we made two organic pesticides formula using essential oil plants and soursop leaves.
Based on our internet literature research, we found out that lots of plants use as organics pests control. But, we have to sort out the plants that can effectively get rid of pests like grasshoppers and walang sangit. Several of them are actually ingredients from household kitchen such as garlic, lemongrass, ginger, galangal, lemon, betel leaf, etc. These plants contains with essential oils that has low toxic and safe for the host plants. We also found out soursop leaves extract are beneficial to repel grasshoppers. So, we made two organic pesticides formula using essential oil plants and soursop leaves.
making and testing the theories
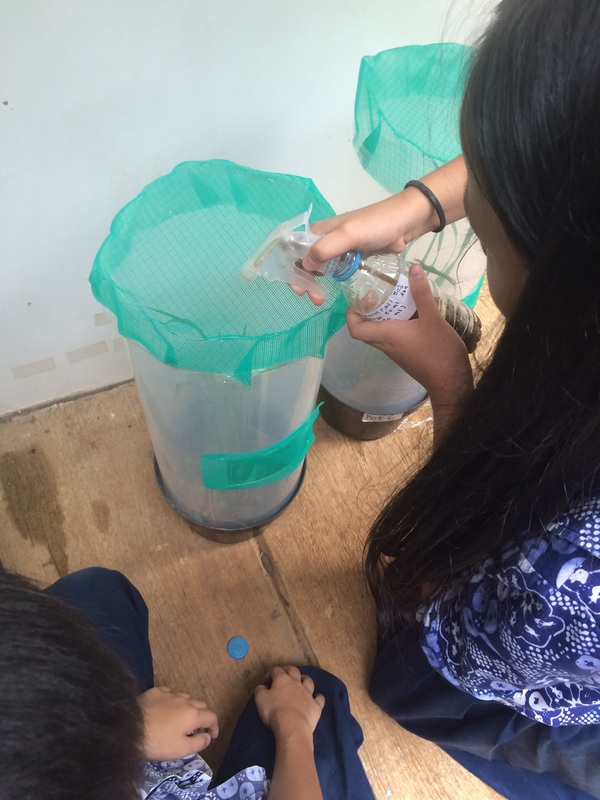
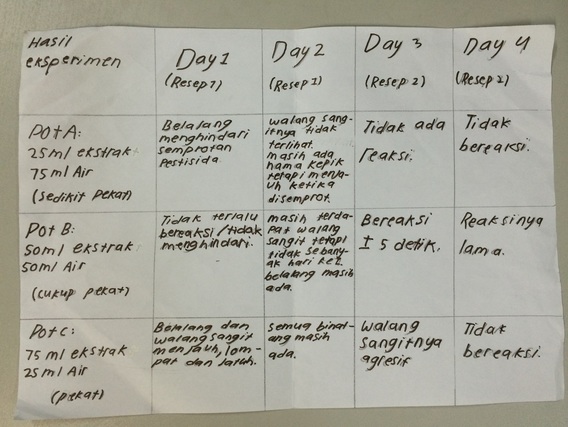
We put the pests in three different flowerpots (Pot A, B, C) with paddy’s plant covered with a plastic cage and gauze on top to prevent the pests escaped. As a replacement of Tomcat or natural predators we used botanical pesticides. We sprayed each flowerpot and observed the pests behavior every day.
observation data
conclusion
1. Botanical pesticides can be use as pests control without harming the sustainability of ecosystem.
2. The pesticides formula can be use as repellent for insect pests.
3. The pests reaction to the pesticides work slowly and often need repetition in the using.
4. The pesticides formula generally work for certain type of pests.
5. The pesticides formula from soursop leaves were more effective to repel paddy pests such as grasshopper and walang sangit.
2. The pesticides formula can be use as repellent for insect pests.
3. The pests reaction to the pesticides work slowly and often need repetition in the using.
4. The pesticides formula generally work for certain type of pests.
5. The pesticides formula from soursop leaves were more effective to repel paddy pests such as grasshopper and walang sangit.
deepening understanding through the application of a concept
For our action we decided to organize workshop about how to make botanical pesticides. We invited 5 different group of people in the school area starts from students council, school gardeners, teachers, parents, and public communities. We share information about Tomcat and the connection to botanical pesticides. We inform them that instead of using chemicals matter to get rid of pests, we use botanical pesticides to maintain the interdependence of paddy field ecosystem because it is save and less toxic to other organism. We also educate them how to make the pesticides from the ingredients prepared.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.