ToPIC: DISADVANTAGE OF LEAD MATERIALS TO PEOPLE AND ENVIRONMENT
HOW THE WORLD WORKS
Central Idea:
Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving and has impact on human life.
Lines of Inquiry:
Key Concepts:
change, connection, responsibility
Learning Outcomes:
"Dan bila kepeda mereka janganlah kamu membuat kerusakan di muka bumi ini mereka menjawab sessunguh nya kami orang-orang yang mengadakan perbaikan”:
QS:al-baqarah ayat 11.
“Telah tampak kerusakan di darat dan di laut disebapkan perbuatan tangan manusia,Allah menghendaki agar mereka merasakan sebagian dari akibat perbuatan mereka agar mereka kembali ke jalan yang lurus”:
QS:ar-rum ayat 41.
Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving and has impact on human life.
Lines of Inquiry:
- How government systems function
- How decision-making practices reflect human rights
- Impact of government on citizens
Key Concepts:
change, connection, responsibility
Learning Outcomes:
- Describe the interactions of living things within and between living things and non-living parts of the environment
- Examine interactions between living things and non-living parts of the environment
- Recognize that solar energy sustains ecosystems through a transformation of energy
- Investigate the conservation of energy in ecosystems
- analyze the effects of changing a link in a food web
- explain how human activities can have positive on local and other environments
"Dan bila kepeda mereka janganlah kamu membuat kerusakan di muka bumi ini mereka menjawab sessunguh nya kami orang-orang yang mengadakan perbaikan”:
QS:al-baqarah ayat 11.
“Telah tampak kerusakan di darat dan di laut disebapkan perbuatan tangan manusia,Allah menghendaki agar mereka merasakan sebagian dari akibat perbuatan mereka agar mereka kembali ke jalan yang lurus”:
QS:ar-rum ayat 41.
|
Mentors with students
|
Mentors with parents and students
|
STEP 1: IDENTIFYING GLOBAL SIGNIFICANT ISSUES
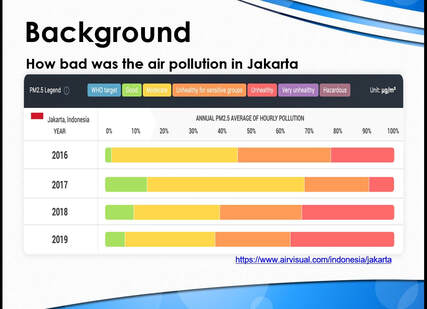
Jakarta had the worst air quality in the world, according to AirVisual, an air quality monitoring app. With an Air Quality Index (AQI) of 210, Indonesia’s capital easily ranked above other notoriously polluted cities, such as Beijing, Dubai, and New Delhi.
So, when we discuss about worst quality of Jakarta, when will it end to a discussion or we can do something as our action to reduce the air pollution?
That's why the students choose the topic " How to reduce air pollution" as their concern in their exhibition.
So, when we discuss about worst quality of Jakarta, when will it end to a discussion or we can do something as our action to reduce the air pollution?
That's why the students choose the topic " How to reduce air pollution" as their concern in their exhibition.
The students joined a seminar in @america, Pacific Place Mall, South Jakarta on January 30th, 2020. They gained a lot of information that can be use as our prior knowledge, how to reduce mercury emissions from coal in Indonesia, what the effects from the air pollution are, what the solution is, etc.
|
|
|
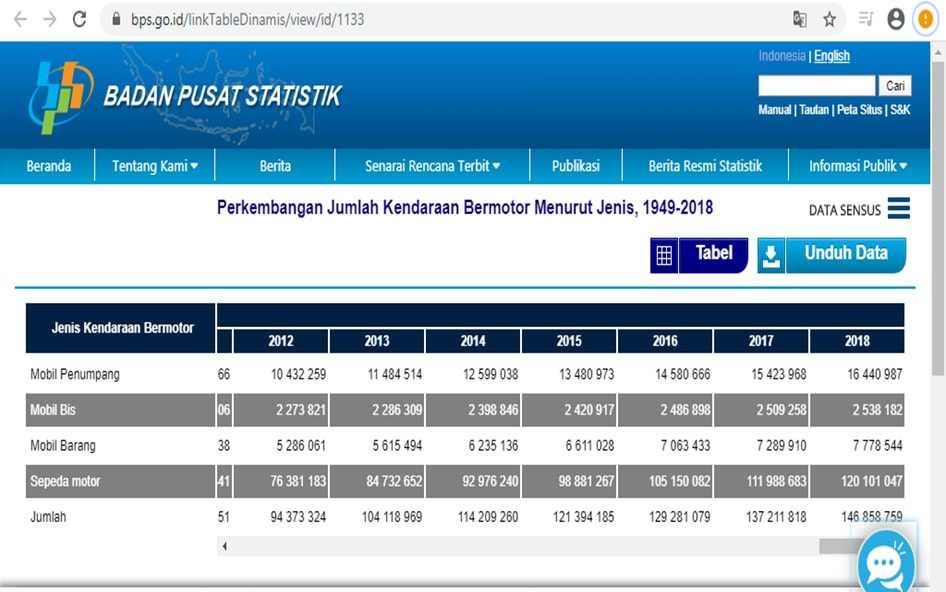
The students did an experiment to check the air pollution around our school and our home. Based on the pollution catcher experiment, they get know that air quality in Jakarta worst and one of the cause of air pollution is emissions from transportation, motor cycle. It proves when the students also put the pollution catcher in one of the mentor's motor cycle.
STEP 2: DETERMINING TIMING AND TIME FRAME

Making Connections Between Previous Learning and Current Learning
Prior Knowledge:
•K2: Transportation
Students learnt about transportation when they were in K2 and it relates to their exhibition topic, how the transportation also affect to the air pollution, and also which transportation that contain lead materials produce air pollution.
•G2: Building and structure, and Natural habitat.
Students learnt about building & structure, also natural habitat when they were in G2. It connects how the building and structure give effect to the air pollution because of lead materials and its influence to the natural habitat.
•G3: Human body system.
Students learnt about human body system when they were in G3 and it relates how the effect of lead materials to human health.
•G4: Economic activity.
Students learnt about economic activity when they were in G4 and it relates how human and economic activities can have negative impact to environment.
Prior Knowledge:
•K2: Transportation
Students learnt about transportation when they were in K2 and it relates to their exhibition topic, how the transportation also affect to the air pollution, and also which transportation that contain lead materials produce air pollution.
•G2: Building and structure, and Natural habitat.
Students learnt about building & structure, also natural habitat when they were in G2. It connects how the building and structure give effect to the air pollution because of lead materials and its influence to the natural habitat.
•G3: Human body system.
Students learnt about human body system when they were in G3 and it relates how the effect of lead materials to human health.
•G4: Economic activity.
Students learnt about economic activity when they were in G4 and it relates how human and economic activities can have negative impact to environment.
step 3: engaging support from the learning community
|
Collecting Data and Reporting Finding/Researching and Seeking Information
We went to KPBB ( Komite Penghapusan Bensin Bertimbel) to collect information about how KPBB collaborate with the government in managing lead gasoline and solution for air pollution that caused by it. The result was KPBB succeeded in convincing the government to collaborate in managing lead. The gasoline from PERTAMINA no longer using lead. KPBB also organized workshop to educate people the danger of lead gasoline and how to reduce air pollution. In PERTAMINA, students learned about other solution in producing less pollution gasoline by mixing 30% palm oil with 70% gasoline, and the product name is B30. |
STEP 4: organizing and learning
|
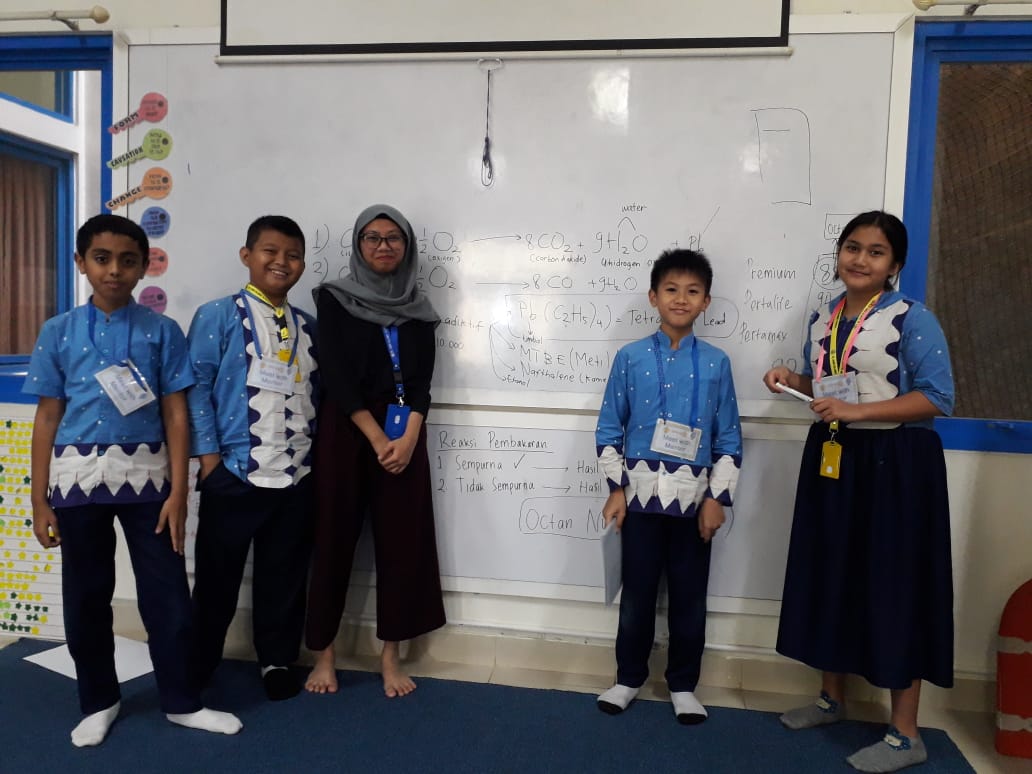
The gasoline that powers the vehicle doesn't occur naturally like water in a stream. So where does it come from? Gasoline actually must be produced from a thick, dark substance pumped from deep underground. We call that substance crude oil or petroleum. The students learned about the composition of gasoline from Ms. Beta, she has background in chemical study and know about the lead materials. They also learnt about octane number. The octane rating or number is a measure of the resistance of gasoline and other fuels to detonation (engine knocking) in spark-ignition internal combustion engines. High-performance engines typically have higher compression ratios and are therefore more prone to detonation, so they require higher octane fuel. A lower-performance engine will not generally perform better with high-octane fuel, since the compression ratio is fixed by the engine design. The octane number of a fuel is measured in a test engine, and is defined by comparison with the mixture of iso-octane and normal heptane which would have the same anti-knocking capacity as the fuel under test: the percentage, by volume, of iso-octane in that mixture is the octane number of the fuel. For example, gasoline with the same knocking characteristics as a mixture of 90% iso-octane and 10% heptane would have an octane rating of 90. Because some fuels are more knock-resistant than iso-octane, the definition has been extended to allow for octane numbers higher than 100. |
STEP 5: monitoring the exhibition
STEP 6: sharing the exhibition
consider action on learning
"Social Entrepreneurship, Participation, and life style choice"
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Link of Students Presentation
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1JLzN0znZh2qpHyA4rWivwsSGj8WCOfJ9