Indonesian orchid biodiversity conservation using tissue culture techniques
How The Word Works
DISCIPLINARY THEME:
natural world and its laws; the interaction between the natural world (physical and biological) and human societies; how humans use their understanding of scientific principles; and the impact of scientific and technological advances on society and on the environment.
Central Idea:
Understanding of Scientific Knowledge is Constantly Evolving and has Impact on Human Life
Lines of inquiry:
- How government systems function
- How decision-making practices reflect human rights
- Impact of government on citizens
Students
mentors
STEP 1
Identifying global significant issues
|
From articles the students found that Indonesia is rich in Endemic Orchids (Orchidaceae), Indonesia is home to one tenth of the world's endemic orchids. Some scientists believe Indonesian orchids reach 5000 - 6000 species. One of the local orchids, the moon orchid (Phalaenopsis amabiis) is even designated as Puspa Pesona or national flower of Indonesia a symbol of the characteristics of the Indonesian nation and state.
With its diversity, orchids can be found in various ecosystems in Indonesia, both in the forest, karst, and other ecosystems. Orchids, which are not only beautiful, are also seen to contain benefits for beauty, medicine, food ingredients and other benefits. Unfortunately, many orchids have been extinct before they were discovered due to forest destruction, endemic orchid habitat. Natural disasters, climate change, deforestation, land use change and theft of genetic resources threaten the preservation of this protected flora. The students discussed and decided that saving and preserving orchid germplasm is a priority that must be done. And the students decided to research more about endemic orchids conservation. |
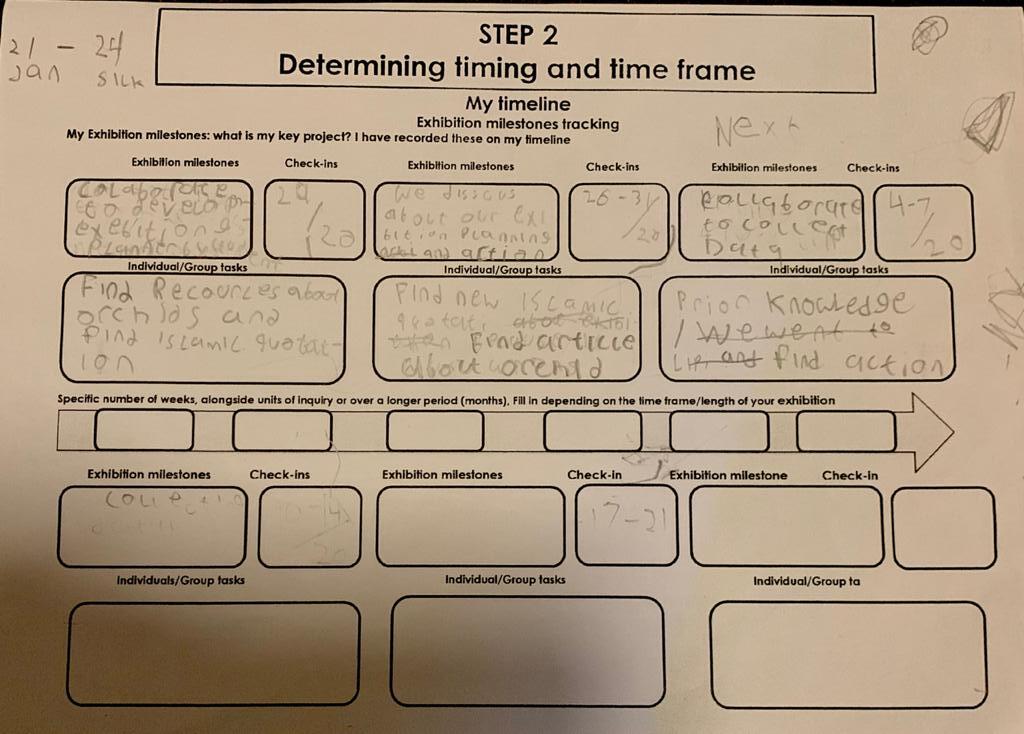
STEP 2
Determining timing and time frame
STEP 3
Engaging support from the learning community
|
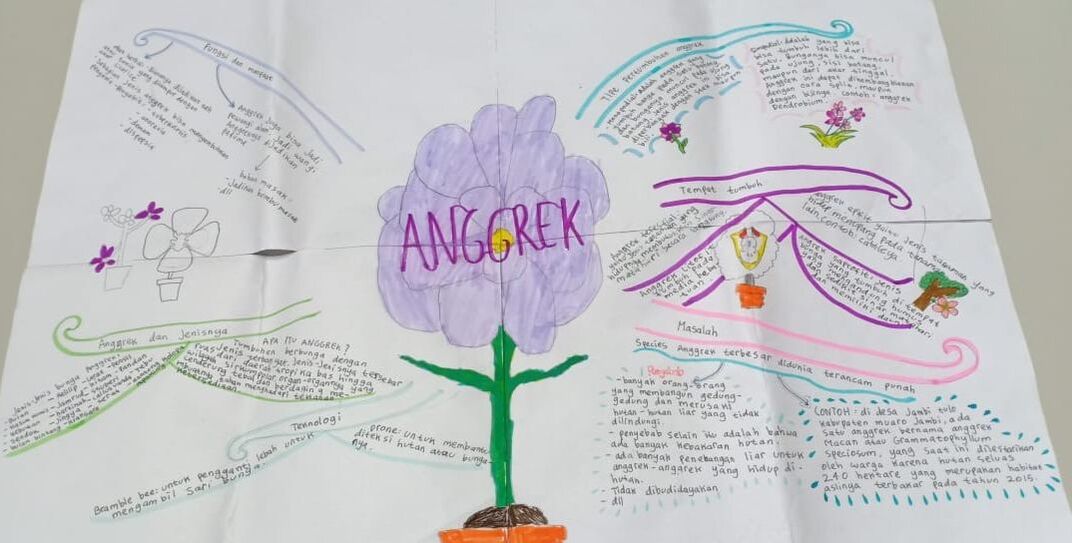
The students read several articles, and made a mind mapping. They found many benefits of orchids for human life. Besides being beautiful, orchids can be used for medicine. Such as a medicine for tuberculosis, anti-cancer prevention, joint pain, nerve disorders in the brain, asthma, ulcer drugs etc. For cosmetics, it is used for anti-aging, skin moisturizer, and perfumes.
In some countries, orchids are also used as food and cooking spices. As for the environment, the orchid is useful as a guaranteed absorbent and keeps fresh air. If orchids become extinct, then we will lose the source of ingredients of medicines, food and cosmetics. |
|
Al Qur’an Quotes:
Qs. Al- Fatir verse 27 أَلَمْ تَرَ أَنَّ اللَّهَ أَنْزَلَ مِنَ السَّمَاءِ مَاءً فَأَخْرَجْنَا بِهِ ثَمَرَاتٍ مُخْتَلِفًا أَلْوَانُهَا ۚ وَمِنَ الْجِبَالِ جُدَدٌ بِيضٌ وَحُمْرٌ مُخْتَلِفٌ أَلْوَانُهَا وَغَرَابِيبُ سُودٌ Do you not see that Allah sends down rain from the sky, and We produce thereby fruits of varying colors? And in the mountains are tracts, white and red of varying shades and [some] extremely black. |
Konservasi Anggrek diatur dalam Undang-undang:
|
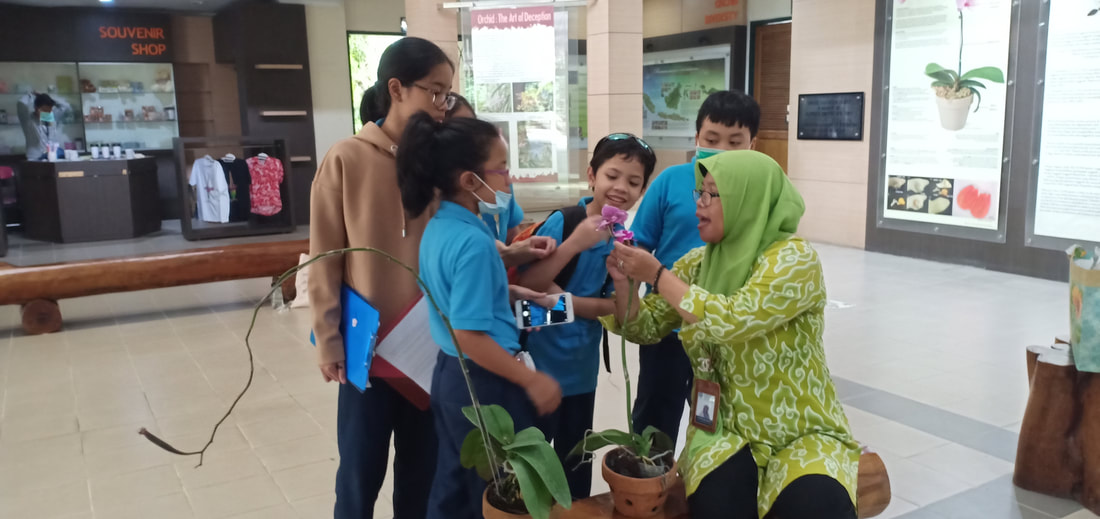
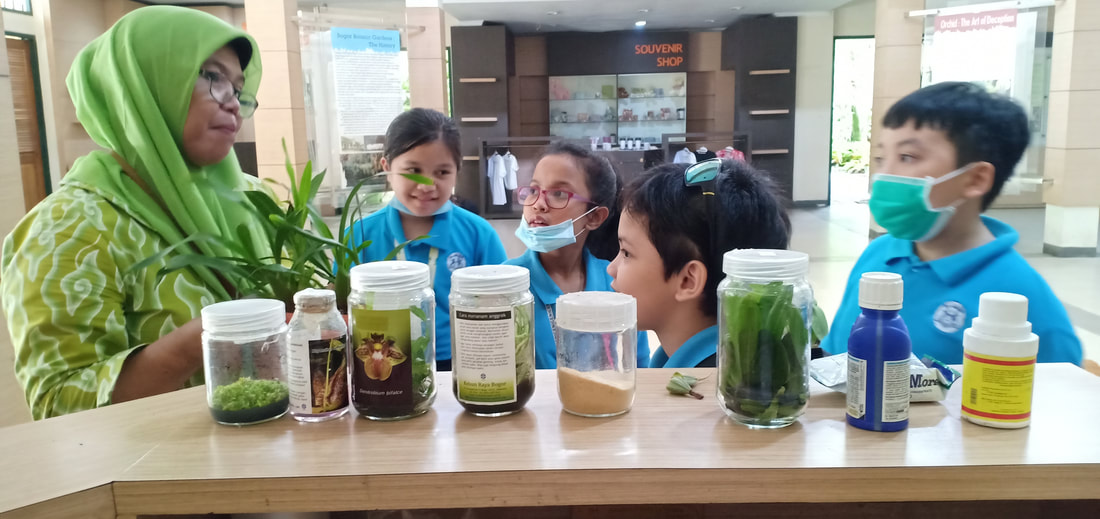
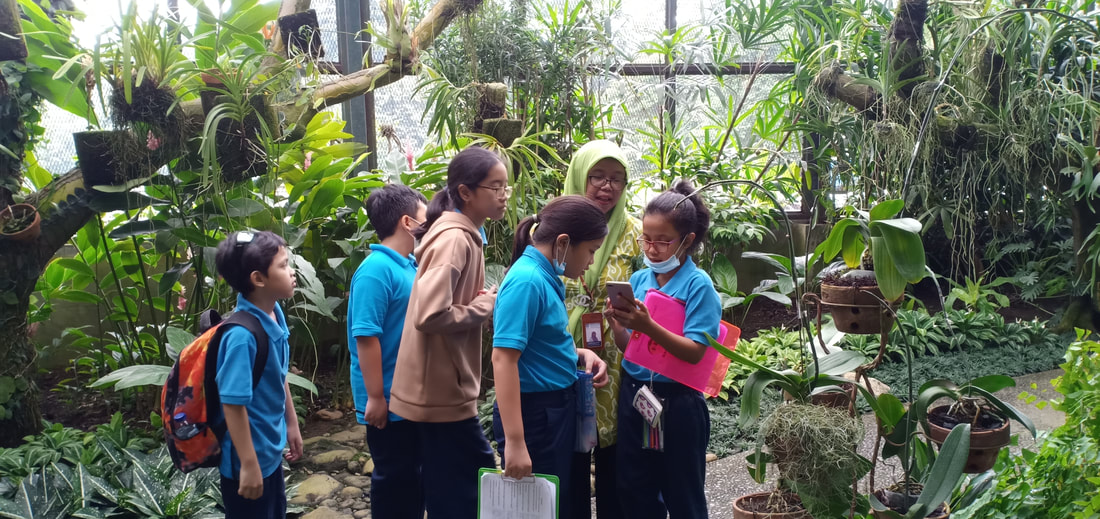
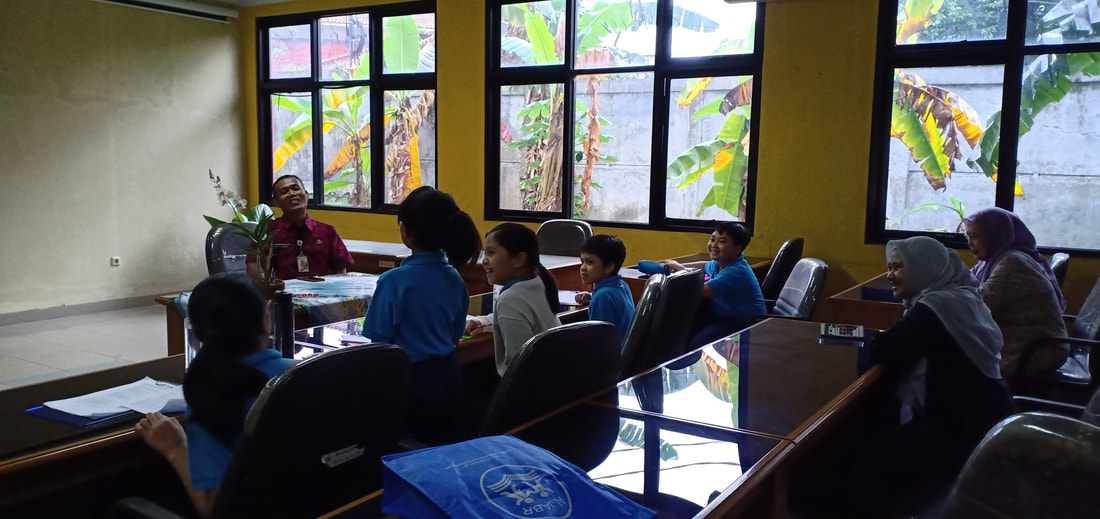
Field trip to Griya Anggrek Kebun Raya Bogor
Pusat Konservasi Tumbuhan Kebun Raya LIPI
|
The students went to the Botanical Gardens Conservation Center-LIPI. They met Mrs. Suprih, the botanist. Mrs. Suprih said that LIPI held expeditions to explore Indonesia's forests to collect orchid species and look for new orchid species in the wild. LIPI has explored forests throughout Indonesia. From Sumatra to Papua. The island that has the most biodiversity of orchids is Papua. Wild orchids found were researched and bred in the Bogor Botanical Garden about 690 species. Of these orchids there are 83 species that are cultured in tissue culture. Types of natural orchids are also interbreeding to get orchids that have large and beautiful flowers, are disease resistant and are easy to plant. Cross-breeding orchids, called hybrid orchids, were developed for cut flowers in the horticulture industry.
|
Wild orchids in Griya Anggrek Kebun Raya Bogor
|
|
|
Pollination of orchids naturally in nature is helped by insects. The seeds are generally almost microscopic and very numerous, in some species over a million per capsule. After ripening, they blow off like dust particles or spores.
They lack endosperm and must enter symbiotic relationships with various mycorrhizal basidiomyceteous fungi that provide them the necessary nutrients to germinate, so all orchid species are mycoheterotrophic during germination and reliant upon fungi to complete their life cycles. |
As the chance for a seed to meet a suitable fungus is very small, only a minute fraction of all the seeds released grow into adult plants. In cultivation, germination typically takes weeks. So, scientists developed technology to culture plant in mass production called tissue culture. With tissue culture technique allows us to culture orchids in mass.
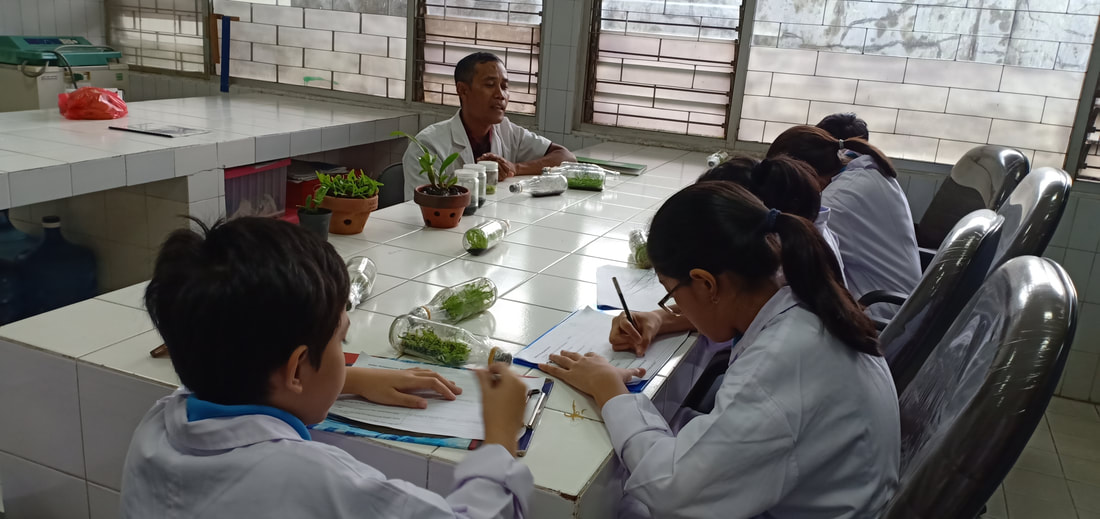
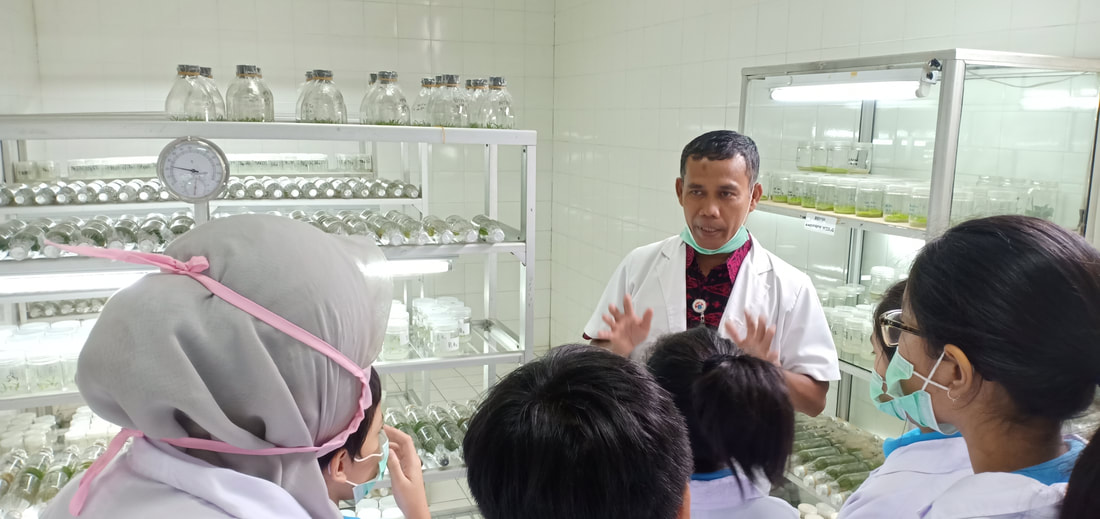
Field trip to Kebun Bibit dan Laboratorium Kultur Jaringan Lebak Bulus
|
The students visited to Lebak Bulus Tissue Culture Laboratory. They met Mr Adji, an orchid tissue culture expert. He explained that tissue culture is process of plant cultivation that aseptically isolates plant part to grow into new plant. The tissue culture technique in orchid was discovered by Knudson in 1922. This technique is used for large scale plant multiplication, especially high-value plants.
In Indonesia, the plants that are usually cultivated using tissue culture are orchids, bananas, teaks, sandalwood trees and gaharu trees. In this laboratory performed tissue culture on orchids and bananas. |
|
STEP 4
ORGANIZING THE LEARNING
STEP 4
ORGANIZING THE LEARNING
After they visited some resources they sorted the information and made reflection
Reflection of field trip to Griya Angrek, Pusat Konservasi Tanaman Kebun Raya Bogor
Reflection of field trip to Kebun Bibit dan Labolatorium Kultur Jaringan Lebak Bulus.
Experimenting and playing with possibilities
|
Experiment 1: Reflasking / Over planting
Transfer and thinning protocorms/seedling to new culture bottle. Question Can the protocorms grow bigger on new medium. Hypothesis Protocorms/ seedlings need to transfer to fresh medium for continued growth. Material - culture bottle - tweezers - medium - autoclave - spatula - Spiritus lamp - alcohol sprayer - laminair air flow cabinet - Petri dishes Procedure
Result
|
Experiment 2: Acclimatization
Transfer of explants from the aseptic chamber (culture bottle) to the community pot (compote) Question Can plantets adapt to new environments (green houses)? Hypothesis Plantets can adapt and grow in new environments by using a hood (coconut fiber). Material - plantets - rubber bracelet - coconut fiber - water - hook - baskets and old newspaper Procedure
|
Taking and defending a position
Analyzing and linking to themselves and their environment
STEP 5
MONITORING THE EXHIBITION
Solving problems in a variety of ways
Making an informed decision to do something
Making an informed decision to do something
|
The students held an orchid exhibition entitled PESONA ANGGREK INDONESIA. They exhibited a variety of wild and hybrid orchids. Visitors can enjoy the beauty of orchids. After that they can buy orchids at the bazaar. The orchid bazaar is visited by teachers, parents, PYP and MYP students. All bought up orchids.
Students from grade 1 to grade 4 were very enthusiastic in taking art-crafting and drawing classes. They were drawing and making pop up card orchid. Hopefully with this activity they will like and want to grow orchids. Live music presents orchid-themed songs and Indonesian beauty. |
|
|
Art and craft activities
|
Bazaar: The visitors can buy hybrid and wild orchids. About 75 pot orchids sold out.
|
STEP 6
SHARING THE EXHIBITION
Alhamdulillah
Thank you
Thank you