Students
Mentors
Central Idea
|
Biodiversity relies on maintaining the interdependent balance of organism within systems
Lines of Inquiry
• Ways in which ecosystems, biomes and environments are interdependent • How human interaction with the environment can affect the balance of systems • The consequences of imbalance within ecosystems |
1. Exploring, wondering, and questioning
|
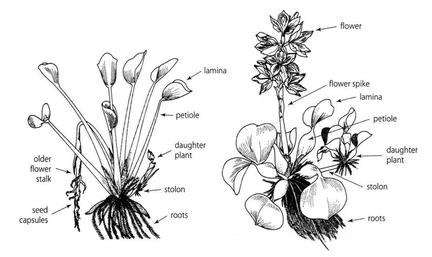
We started our project by making a mind map. We wrote everything we knew about water hyacinth (eceng gondok); such as, the characteristic of water hyacinth, how it grew, and the bad effects of it to the habitat around.
|
|
2. Researching and seeking information
We tried to find out about water hyacinth on the internet to confirm if the knowledge we got was true or not.
We tried to find out about water hyacinth on the internet to confirm if the knowledge we got was true or not.
|
https://taxo4254.wikispaces.com/Eichhornia+crassipes
|
Facts about water hyacinth:
|
3. Collecting data and reporting findings
To deepen our knowledge about water hyacinth, we visited Balingbagdias Kementrian Kelautan dan Perikanan, Depok. There, we learned a lot about water hyacinth especially about the characteristics, how it grew, the bad effects of water hyacinth, and how to overcome the spread of water hyacinth.
To deepen our knowledge about water hyacinth, we visited Balingbagdias Kementrian Kelautan dan Perikanan, Depok. There, we learned a lot about water hyacinth especially about the characteristics, how it grew, the bad effects of water hyacinth, and how to overcome the spread of water hyacinth.
4. Deepening understanding through application of knowledge
Why is Water Hyacinth considered to be a nuisance?
Why is Water Hyacinth considered to be a nuisance?
- Physical Problems - Water hyacinth mats clog waterways, making boating, fishing and almost all other water activities impossible. Water flow through water hyacinth mats is greatly diminished, an acre of water hyacinth can weigh more than 200 tons.
- Ecological Impacts - Water hyacinth mats degrade water quality by blocking photosynthesis, which greatly reduces oxygen levels in the water. This creates a cascading effect by reducing other underwater life such as fish and other plants. Water hyacinth also reduces biological diversity, impacts native submersed plants, alters immersed plant communities by pushing away and crushing them, and also alter animal communities by blocking access to the water and/or eliminating plants the animals depend on for shelter and nesting.
How can we prevent the spread of Water Hyacinth?
5. Experimenting and playing with possibilities
We conduct our experiment using 3 aquariums to observe 3 different ways to prevent water hyacinth from growing rapidly. From our experiment, we are able to conclude that herbicide is not a good choice to prevent the spread of water hyacinth because it will damage the ecosystem.
Using grass carp fish is the safest way to control the growth of water hyacinth because grass carp fish is herbivore fish. It only eats the plants especially water hyacinth.
- Mechanical control: Water hyacinth removal by hand or machine is a practical control method often used for small areas or when numbers are low. Physical removal is most effective for small infestations and should be made before flowering and seed set in October.
- Herbicide control: Before using any herbicide always read the label carefully. All herbicides must be applied strictly in accordance with the directions on the label. When treating water that is used for irrigation purposes, the withholding period should be followed in accordance with the label recommendations. Spraying an entire heavy infestation can cause water hyacinth to sink and result in pollution from the rotting weed.
- Grass carp control: Grass carp naturally eat water hyacinth.
5. Experimenting and playing with possibilities
We conduct our experiment using 3 aquariums to observe 3 different ways to prevent water hyacinth from growing rapidly. From our experiment, we are able to conclude that herbicide is not a good choice to prevent the spread of water hyacinth because it will damage the ecosystem.
Using grass carp fish is the safest way to control the growth of water hyacinth because grass carp fish is herbivore fish. It only eats the plants especially water hyacinth.
6. Taking and defending a position
Not many people know about grass carp fish. So, as our action, we shared our information about grass carp fish as a solution to control the growth of water hyacinth in SMA 106 Pekayon, East Jakarta.
Not many people know about grass carp fish. So, as our action, we shared our information about grass carp fish as a solution to control the growth of water hyacinth in SMA 106 Pekayon, East Jakarta.
Here we are! in our exhibition!